SEO, like most Internet marketing specialties, has a language all its own. The definitions below will give business leaders a better understanding of the very important ideas behind key SEO terms, and help them evaluate SEO agencies and campaigns more confidently.
SEO, like most Internet marketing specialties, has a language all its own. The definitions below will give business leaders a better understanding of the very important ideas behind key SEO terms, and help them evaluate SEO agencies and campaigns more confidently.
1. 301 Redirect. A 301 redirect is Google’s preferred method of automatically taking visitors to an old URL or (sometimes) a URL with duplicate content to the current, correct page. SEO impact: Points Google to the content you want it to see.
2. ALT Tag. An ALT tag is a bit of HTML code that causes a text description of an image to display when the image itself does not display on the screen. SEO impact: Google bots read ALT tags, giving your images better organic visibility when they are optimized
3. Anchor Text. Anchor text is the text you click on in a hyperlink. SEO impact: Google looks for natural link text; e.g., text that varies from keywords to the URL to the company name to simply “click here”, etc. Over optimizing anchor text with keywords can negatively affect organic visibility.
4. Authority. “Authority” describes how highly Google regards your website (domain authority) or a particular Web page (page authority). Following White Hat SEO practices has a cumulative effect of increasing domain authority and page authority.
5. Black Hat SEO. Aggressive  SEO practices designed to manipulate organic rankings for short-term results are referred to as Black Hat. SEO impact: Using Black Hat techniques can result in severe penalties and should be avoided at all cost.
SEO practices designed to manipulate organic rankings for short-term results are referred to as Black Hat. SEO impact: Using Black Hat techniques can result in severe penalties and should be avoided at all cost.
6. Canonical URL. When a website(s) has active pages with duplicate content, or multiple URLS for the same page (e.g., SampleURL.com and sampleurl.com) a canonical URL tells Google which page is the main source of the content. SEO impact: Canonical URLs ensure Google points users to the version of a Web page you want them to see.
 7. Content Marketing. Content marketing is an Internet marketing technique where content is used to drive leads and improve branding. SEO impact: Creating high quality on-site and off-site content produces significant SEO impact: Creates natural inbound links and improves domain and page authority.
7. Content Marketing. Content marketing is an Internet marketing technique where content is used to drive leads and improve branding. SEO impact: Creating high quality on-site and off-site content produces significant SEO impact: Creates natural inbound links and improves domain and page authority.
8. Conversion. When a user clicks on an organic link in a search engine, or phones a company using information from an organic link, they are SEO conversions. SEO impact: Conversions are a useful metric for evaluating SEO performance. However – all conversions are not sales leads, so it is extremely important to validate sales leads as part of SEO execution and evaluation.
9. Directory. Directories are websites that display lists of recommended or endorsed websites, usually within a particular niche. SEO impact: Having a directory listing with a link can be very good or very bad for SEO, depending on the authority of the directory website in question.
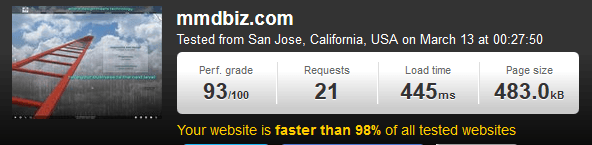
![]() 10. Google Analytics. Google Analytics is a free service that provides highly detailed information and statistics about website performance. SEO impact: Google Analytics provides essential information for SEO, including sources of referred traffic (e.g., traffic sent from Google organic search to the website), and traffic and user behavior on individual website pages.
10. Google Analytics. Google Analytics is a free service that provides highly detailed information and statistics about website performance. SEO impact: Google Analytics provides essential information for SEO, including sources of referred traffic (e.g., traffic sent from Google organic search to the website), and traffic and user behavior on individual website pages.
11. Google Webmaster Tools. Google Webmaster Tools is a free service that allows webmasters to identify and correct website issues that impede SEO performance. SEO impact: Webmaster Tools is invaluable for on-site optimization.
12. Internal Link. Internal links are hyperlinks that link to other pages within a website. SEO impact: A website’s internal linking system, if well constructed, helps Google determine the relative importance of website pages and thus improves search visibility.
13. Keyword Research. Keyword research is the process of systematically reviewing search terms used in organic search and evaluating their potential effectiveness for SEO campaigns. SEO impact: All SEO campaigns must start with detailed keyword research, since an SEO campaign is only as good as the search terms its online content is built around.
14. Keywords. Keywords are the words and phrases search engine users input on Google, Bing and other search engines. SEO impact: Strategically valuable keywords are ones used by people looking for a company’s products and services, but don’t know who the company is or are not aware it sells those particular things.
15. Landing Page. In SEO, a landing page (or entry page) is a website page that search engine users come to after clicking on an organic link. SEO impact: Creating persuasive, informative landing pages for strategically important keywords greatly improves lead generation.
16. Link Acquisition. Link acquisition, also referred to as link building or link development, is the SEO process of acquiring high authority, relevant backlinks to a client website. SEO impact: Link acquisition must be undertaken carefully by firms intimately familiar with best practices — Black Hat techniques can be interpreted as manipulative by Google and do much more harm than good.
17. Link Profile. A website’s link profile is the totality of inbound links pointing to that website. SEO impact: A strong link profile, which is diverse and driven by other websites that desire to link to the website based on the quality and usefulness of its content, has a huge positive impact on SEO performance.
18. Link Reclamation. Link reclamation is the SEO process of identifying poor quality links to a website, and then taking steps to eliminate or improve them. SEO impact: Over time, a website builds up links from websites that have fallen into disfavor with Google or are otherwise undesirable. Cleaning them up improves a website’s link profile and SEO performance.
19. Long Tail Keywords. Long tail keywords are keyword phrases that are highly detailed, often having relatively low search volume but also a very high likelihood of producing conversions, such as “buy 100% organic sunscreen in orlando”. SEO impact: Companies that focus only on high volume keywords rather than including longtail keywords miss significant opportunities to generate sales leads.
20. Meta Description. A Meta description is a snippet of HTML text associated with a Web page that sometimes displays under a link in organic search results. SEO impact: A persuasive Meta description encourages users to a click on a link, thus improving conversions and lead generation.
21. Meta Title. The Meta title of a Web page is HTML code that describes the content of a page. Meta title tags should always be unique, accurate and include important keywords. SEO impact: Well-written Meta titles have great importance in communicating what a page is about to Google. They are probably the most important thing to get right on a website.
22. Off-site Optimization. Off-site optimization is SEO work undertaken away from the website to improve organic search visibility. Tasks include off-site content marketing and directory listing/renewal. SEO impact: To be successful, all SEO campaigns should have a robust off-site component.
23. On-site Optimization. On-site  optimization is SEO work undertaken within the website to improve organic search visibility. Tasks include reviewing Google Webmaster Tools to correct errors and adding strategic website content. SEO impact: To be successful, all SEO campaigns should have a robust on-site component.
optimization is SEO work undertaken within the website to improve organic search visibility. Tasks include reviewing Google Webmaster Tools to correct errors and adding strategic website content. SEO impact: To be successful, all SEO campaigns should have a robust on-site component.
24. Ranking Factor. A ranking factor is something known to be part of the Google Algorithm for the ranking of website content, such as Meta titles. Some factors, such as social media mentions, are not definitive ranking factors, but are instead only correlated to high organic search visibility. SEO impact: A competent SEO company understands the nuances of the many ranking factors and takes them into account for all campaign activity.
25. Robots.txt. Robots.txt is a “behind-the-scenes” file on a website that tells Google “robots” / “bots” / “crawlers” (see spider) to ignore certain content or provides other instructions to them about how to read and interpret the website. SEO impact: Proper use of robots.txt makes it easier for Google to understand and thus give higher visibility to strategically important website pages.
26. Search Algorithm. A search algorithm is a complex “recipe” for evaluating the organic search engine significance of website pages relative to the keywords search engine users input when conducting a search. The most important of these is the Google Algorithm, as Google continues to be the dominant, most widely used search engine. SEO impact: Google’s algorithm changes continually. A competent SEO company keeps pace with algorithm updates, so as not to use outdated techniques that result in neutral or even negative results.
27. SERP. SERP stands for search engine results page. It is the page of links search engine users see after inputting keywords for a search. SEO impact: Today, SERPs are highly customized. Universal search, personalized search and other factors have resulted in SERPS with various types of results on the page, obscuring the meaning of “rankings.” Competent SEO companies thus focus on overall visibility rather than pursue hard to calculate and relatively unimportant ranking numbers.
28. Sitemap. A sitemap is a list of Web pages on a website. For SEO, Google recommends specific sitemap attributes to enable it to better understand and rank a website. SEO impact: A properly structured sitemap has a large role in improving search engine visibility, especially for websites with many pages.
29. Spider. A “spider” is a search engine robot that visits and analyzes a website. Google spiders. SEO impact: Well-optimized websites enable spiders to quickly and correctly interpret its content and thus improve organic search visibility.
 30. White Hat SEO. White Hat SEO practices follow Google guidelines and other established best practices. SEO impact: Using White Hat SEO techniques is the best way to obtain results for SEO campaigns in the long term.
30. White Hat SEO. White Hat SEO practices follow Google guidelines and other established best practices. SEO impact: Using White Hat SEO techniques is the best way to obtain results for SEO campaigns in the long term.
SEO is an foundational part of most Internet marketing strategies. Executives don’t have to be subject matter experts, but the better they understand the principles behind SEO, the better able they are to keep their programs on track.
This article was originally written by Brad Shorr:
Brad Shorr is the B2B Marketing Director of Straight North, a group of Internet marketing experts helping companies of all sizes with their search marketing campaigns.
Cheers,
Marcel Manzardo | President & CEO
MMDesign Business Solutions
phone: 888 885-0205 x400 | fax: 888 422-0186
marcel.manzardo@mmdbiz.com
www.mmdbiz.com